Does the state of Georgia have its hand in your 401(k) when you decide to retire? Yes, in the Peach State, those hard-earned retirement savings are indeed subject to state income tax upon withdrawal, currently at a flat rate of 5.19%. Navigating the nuances of Georgia's tax landscape requires a clear understanding of its various components, from income tax to property assessments, and everything in between. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Georgia's tax system, offering insights into the specific areas that impact residents and businesses.
Understanding Georgia's tax policies is crucial for both financial planning and compliance. The state's approach to taxation is multifaceted, affecting everything from retirement income to everyday purchases. Let's break down the key elements, offering clarity on how these policies shape the financial lives of Georgians.
| Tax Type | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax | Georgia imposes a state income tax on individuals' earnings. | In 2024 (taxes filed in 2025), the state income tax rate is 5.39%. Beginning in 2024, the Georgia income tax changed to a flat rate of 5.49%. From 2025 to 2029, the rate will gradually be reduced to 4.99% if certain economic targets are met. There are no local income taxes in Georgia. |
| Social Security Tax | Georgia does not tax social security benefits. | The state excludes social security income from state taxes. |
| 401(k) Withdrawals | Distributions and withdrawals from a 401(k) plan are subject to state income tax. | The flat rate is currently 5.19%. |
| Retirement Income Exclusion | Eligible individuals can exclude a portion of their retirement income. | Individuals aged 62 or older, or those who are permanently disabled, can exclude up to $65,000 of retirement income per person from their state taxable income in 2024. |
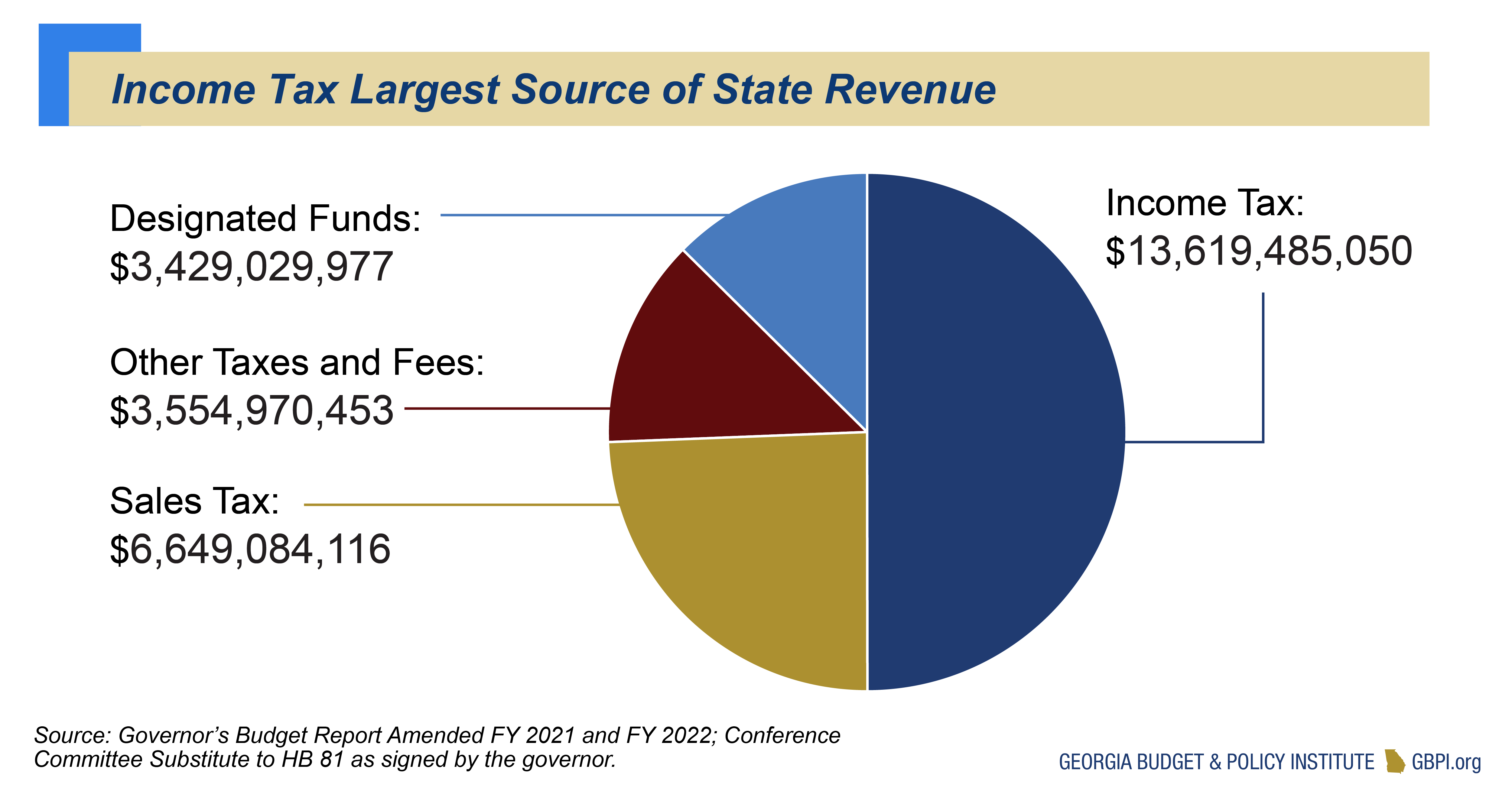
| Sales Tax | Georgia imposes tax on the retail sales price of tangible personal property and certain services. | Local municipalities may tax groceries, which have no state sales tax. Some prescription drugs and medical supplies are exempt. |
| Property Tax | Real estate taxes vary by county and municipality. | The average tax rate was .72 percent of a home's assessed value in 2022, according to the Tax Foundation. Fulton County collects the highest property tax, while Warren County has the lowest. |
| Alcoholic Beverage Tax | Georgia has high taxes on alcoholic beverages. | A $3.79 tax per gallon on distilled spirits and a $0.48 tax per gallon of beer. |
| Gasoline Tax | Georgia charges a tax on gasoline. | The tax rate is 33.05 cents per gallon of gasoline. |
| Estate and Inheritance Tax | Georgia does not have an estate tax or inheritance tax. |
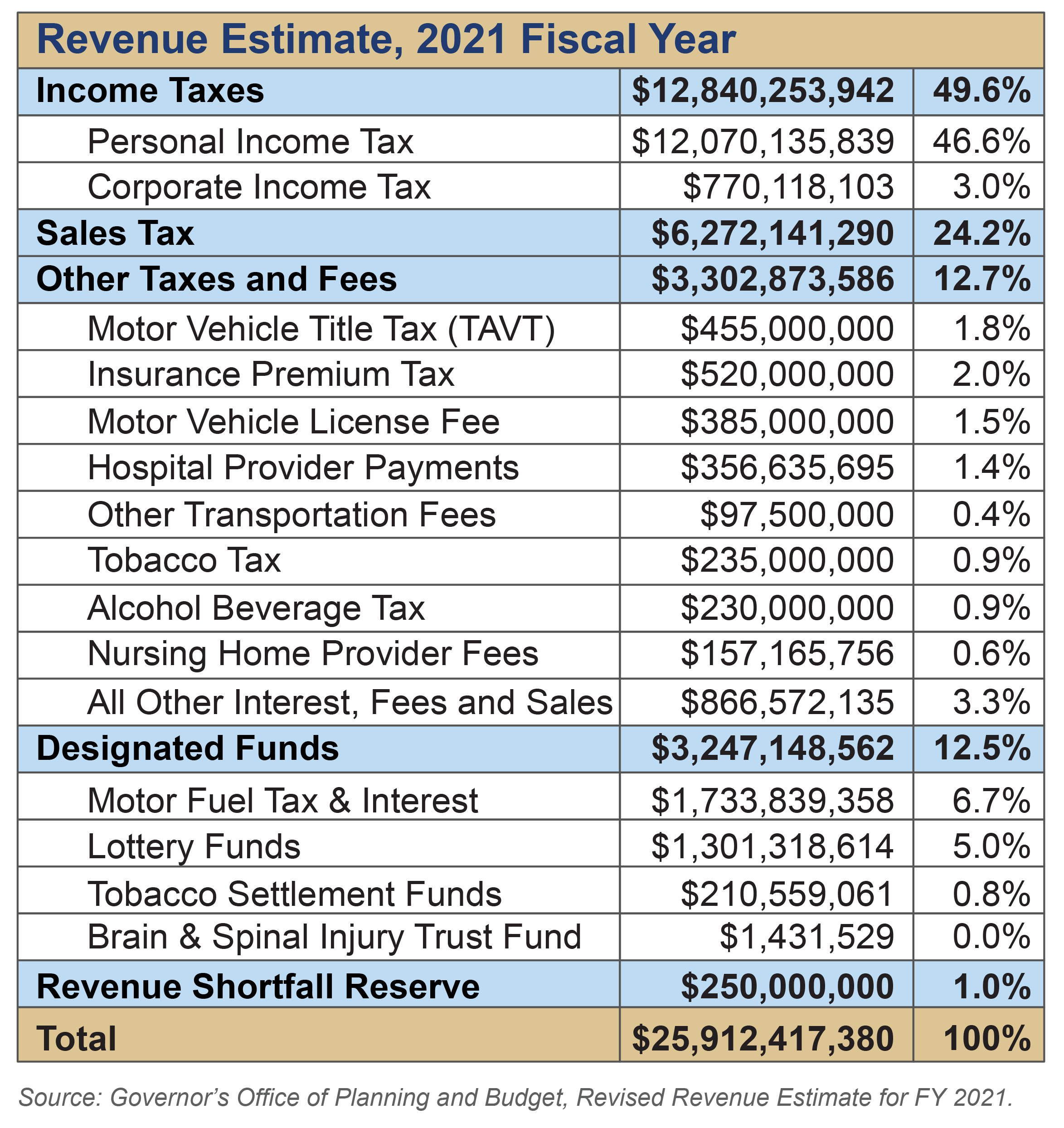
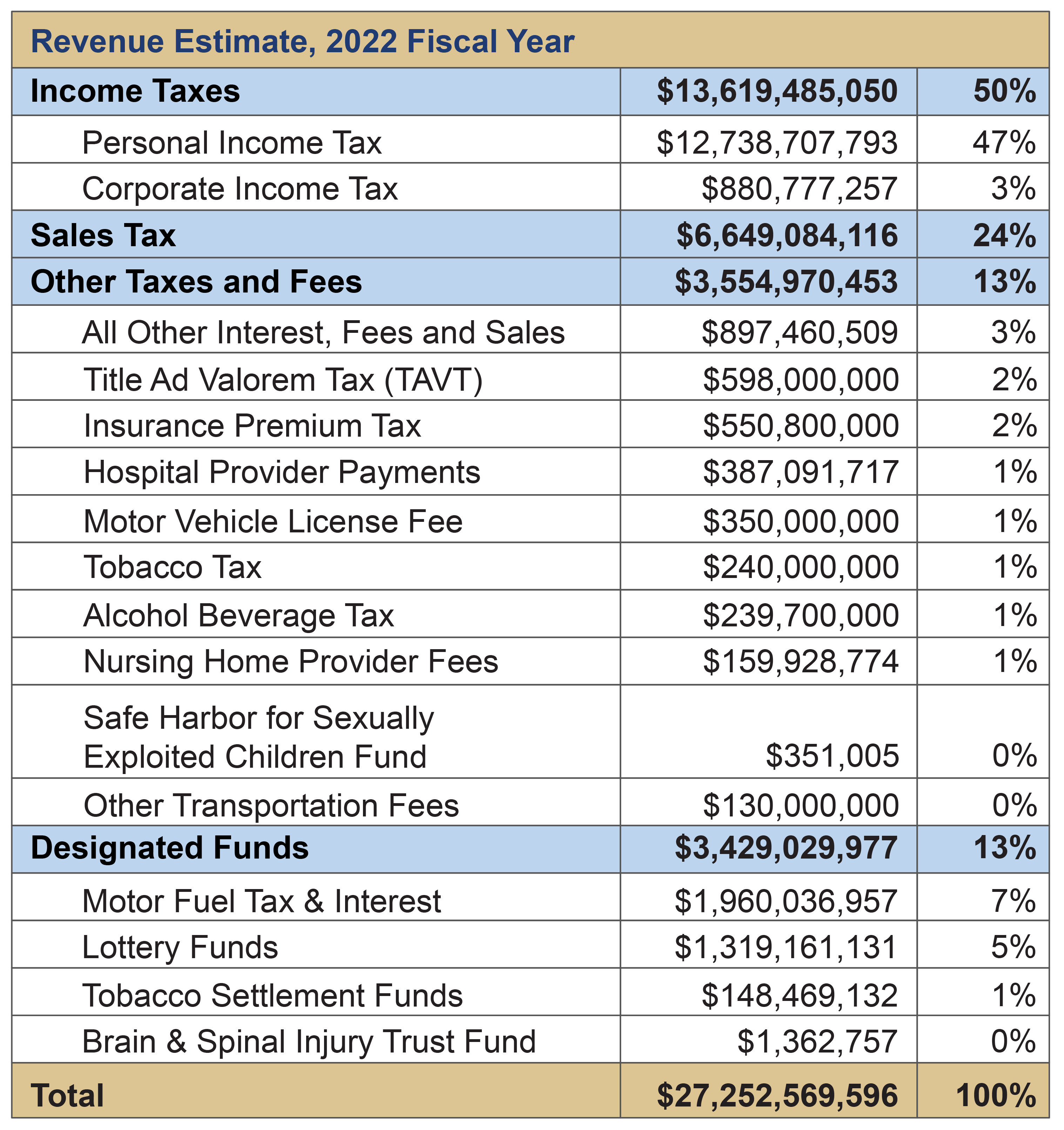
The cornerstone of Georgia's tax system is its income tax. Unlike some states, Georgia currently utilizes a flat income tax system, meaning that all taxable income is taxed at the same rate. As of 2024, the rate is set at 5.49%. However, a gradual reduction is planned, with the rate expected to decrease to 4.99% between 2025 and 2029, provided certain economic targets are achieved. The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) plays a pivotal role in administering these taxes, ensuring that returns are processed accurately and refunds are issued in a timely manner.
For the upcoming tax year (2024, filed in 2025), taxpayers should note the 5.39% income tax rate. Also, taxpayers need to file their 2023 and 2024 taxes prior to receiving any potential surplus income tax refunds, which the DOR is scheduled to start issuing in late May or early June.
Georgia's tax laws also feature exemptions for specific types of income. Perhaps the most notable is the exclusion of social security benefits from state taxes, providing some relief for retirees. Furthermore, the state extends these exclusions to other retirement income sources, including pensions, annuities, and interest income. This proactive measure reflects Georgia's commitment to supporting its senior citizens and disabled residents.
For those aged 62 or older, or those who are permanently disabled, the state allows for a significant exclusion on retirement income. Up to $65,000 of retirement income per person can be excluded from state taxable income in 2024. This is a beneficial aspect, allowing certain taxpayers to minimize their state tax burden.
When it comes to sales tax, Georgia generally imposes this on the retail sales price of tangible personal property and specific services. However, some exceptions exist. Notably, some prescription drugs and medical supplies are exempt, easing the financial burden on those with medical needs. The local municipalities do have the authority to levy taxes on groceries, although these do not incur a state sales tax.
Property taxes in Georgia are administered at the county and municipal levels. These vary considerably, with the exact rate depending on the county where the property is located. Real estate taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, funding essential services such as schools, infrastructure, and public safety. The average effective property tax rate in Georgia is a crucial consideration for homeowners.
Georgia's tax laws don't stop at income and sales taxes; they also include excise taxes on specific items, such as gasoline and alcoholic beverages. The state charges a tax of 33.05 cents per gallon of gasoline, and the tax rates on alcoholic beverages are notably high compared to some other states. For distilled spirits, a tax of $3.79 per gallon is levied, while beer is taxed at $0.48 per gallon.
Georgia's tax system has been subject to various legislative changes. House Bill 581, passed during a recent legislative session, is one such example. The Georgia General Assembly also passed House Bills 111 and 112, impacting income tax rates and deductions. Amendments to tax administration instructions are periodically issued, reflecting the dynamic nature of tax regulations.
Taxpayers in Georgia have access to a valuable resource known as the Georgia Tax Center (GTC). This online portal is a secure and convenient way for individuals and businesses to manage their state tax obligations. Through the GTC, taxpayers can file returns, make payments, and access important tax information. Sales tax numbers can be verified using the sales tax ID verification tool available through this platform, enhancing transparency and accuracy.
The state of Georgia provides numerous resources for understanding its tax system. From the official Department of Revenue website to various online guides, residents have access to information to help them comply with the law. Understanding the key components of Georgia's tax system is crucial for compliance, financial planning, and maximizing potential tax savings. Consulting with a tax professional can further assist in navigating the complexities of Georgia's tax landscape.
As of January 1, 2024, several additional tax changes took effect. The Georgia standard deductions have increased to $24,000 for taxpayers filing married jointly, offering potential tax savings for many families. These modifications reflect the state's ongoing efforts to adjust its tax policies and improve the overall tax experience for its residents.
The due date for Georgia individual income tax returns is typically April 15th, unless an extension is filed or the governor extends the deadline. However, it's essential to keep track of these deadlines and any changes announced by the state.
For those involved in property or rental tax, the rules vary. For leasing companies engaged in financial, not operational leases, the tax rate can range from 0% to 1%, depending on household income and the municipality where the property is located. This highlights the importance of understanding the specifics of the tax regulations that apply to your situation.
Georgia's tax system offers a mix of simplicity and complexity. While the flat income tax rate simplifies the process, the variations in sales, property, and excise taxes necessitate a closer look. As the state continues to refine its tax policies, it is important to stay informed and take advantage of available resources. The Georgia Department of Revenue is dedicated to providing guidance and support for taxpayers to ensure they meet their obligations.
In addition to the state-level taxes, the article provides information on local taxes. Local municipalities may tax groceries, but there is no state sales tax on them. Also, local municipalities may add an extra 4.9% in taxes.
One essential aspect of Georgia's tax landscape is its commitment to supporting its residents. By excluding social security benefits from state taxes, the Peach State aims to provide financial relief to its retirees. This measure is a key component of the state's overall tax strategy.
Georgia's tax system has various tax brackets, which affects the income tax. As of 2025, the maximum marginal income tax is 5.750% and the income tax rate is 5.49% flat.